how is blood sugar regulated by negative feedback Blood glucose control level summary concentration
Our body is an incredible machine that is capable of regulating its own functions to maintain a state of balance and stability, known as homeostasis. One of the vital processes that our body ensures to keep in check is the regulation of blood sugar levels. This is vital because any major fluctuations in blood sugar levels can have serious consequences on our overall health and well-being.
Homeostasis of Glucose Levels
One of the key players in the regulation of blood sugar levels is a phenomenon known as negative feedback. Negative feedback mechanisms act as a control system that helps maintain stability and prevent drastic changes. In the case of blood sugar regulation, this involves a delicate balance between the levels of glucose in the bloodstream and the hormones that control its uptake and storage.
To better understand this process, let’s take a closer look at the role of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When blood sugar levels rise after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin acts as a key, unlocking the cells in our body to allow glucose to enter and be utilized for energy. This, in turn, helps lower blood sugar levels to maintain a state of balance.
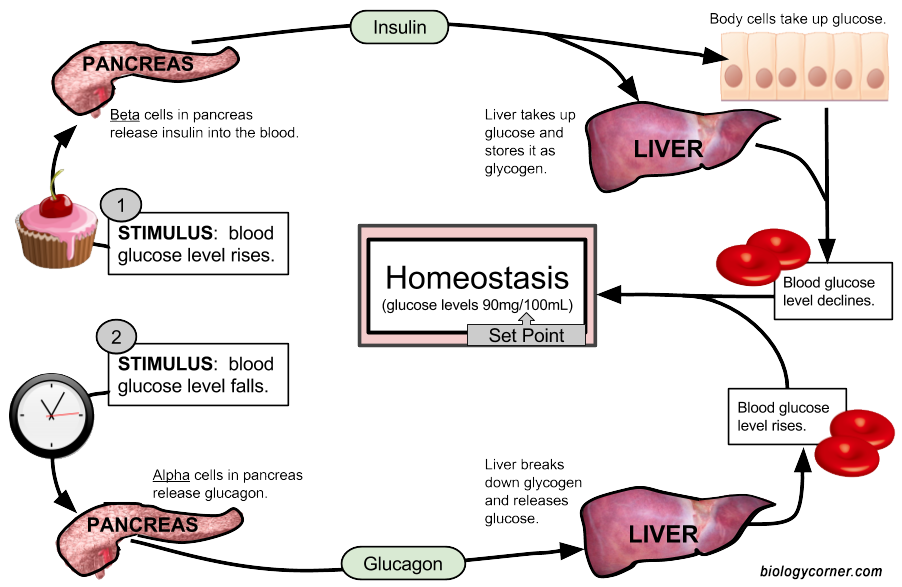
However, if blood sugar levels drop too low, another hormone called glucagon is released by the pancreas. Glucagon instructs the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream, raising blood sugar levels back to normal. This intricate dance between insulin and glucagon ensures that blood sugar levels are kept within a healthy range.
Positive Feedback: Balancing Act
While negative feedback plays a significant role in blood sugar regulation, positive feedback also has its place in maintaining balance. Positive feedback mechanisms amplify or further enhance a particular process. In the case of blood sugar regulation, positive feedback comes into play when blood sugar levels rise above the normal range.

When blood sugar levels spike, the body responds by releasing a hormone called adrenaline. Adrenaline signals the liver to convert even more glycogen into glucose, releasing more of it into the bloodstream. This surge of glucose provides a burst of energy, helping the body deal with the immediate stressor and bringing blood sugar levels back to the desired range.
However, it is important to note that prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including type 2 diabetes. In this condition, the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, resulting in persistently high blood sugar levels.
It is truly fascinating how our body maintains such intricate systems to regulate blood sugar levels and ensure homeostasis. By continuously fine-tuning the delicate balance between negative and positive feedback mechanisms, our body ensures that blood sugar levels remain within the optimal range for our overall health and well-being.
So the next time you enjoy a meal or feel a surge of energy, take a moment to appreciate the incredible complexity of blood sugar regulation and how our body tirelessly works to maintain its delicate balance.
If you are looking for Hormones · Anatomy and Physiology you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Hormones · Anatomy and Physiology like #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level, Hormones · Anatomy and Physiology and also Hormones · Anatomy and Physiology. Read more:
Hormones · Anatomy And Physiology
 philschatz.comfeedback hormones negative loop endocrine physiology system control stress pathways hormone glucocorticoid regulation release anatomy gland adrenal hypothalamus glucocorticoids loops
philschatz.comfeedback hormones negative loop endocrine physiology system control stress pathways hormone glucocorticoid regulation release anatomy gland adrenal hypothalamus glucocorticoids loops
️ Homeostasis Blood Sugar Regulation. Homeostasis Of Glucose Levels
 legendofsafety.comblood homeostasis regulation glucose sugar feedback loop levels insulin positive glucagon diabetes pancreas control loops endocrine liver decreases decrease
legendofsafety.comblood homeostasis regulation glucose sugar feedback loop levels insulin positive glucagon diabetes pancreas control loops endocrine liver decreases decrease
#113 The Control Of Blood Glucose | Biology Notes For A Level
 biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control level summary concentration
biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control level summary concentration
An Explanation Of Motivation In Terms Of Homeostasis Is Best
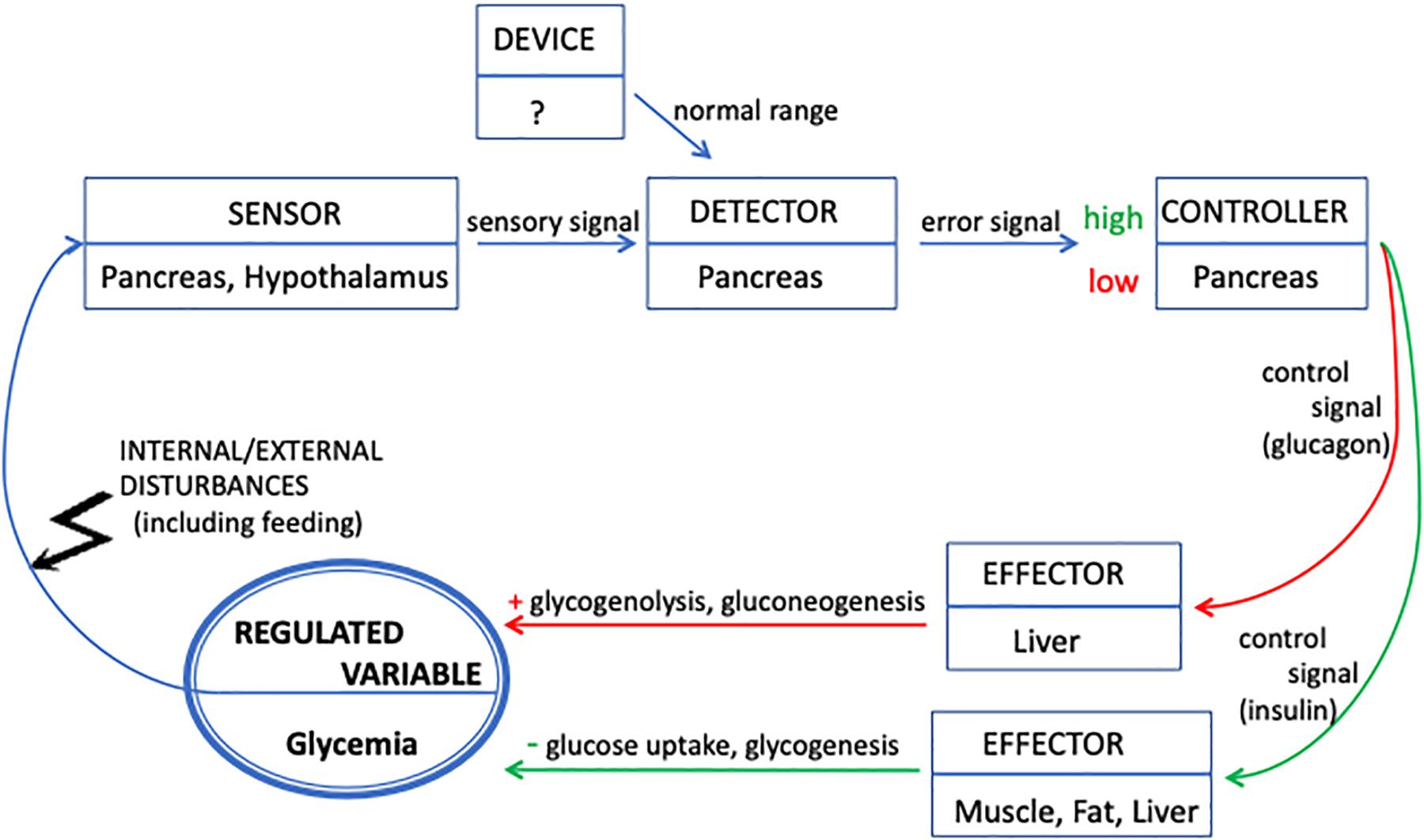 captionsenergyca.blogspot.comglycemia homeostasis loops organizational frontiers physiology illustrated
captionsenergyca.blogspot.comglycemia homeostasis loops organizational frontiers physiology illustrated
Is Blood Sugar Regulated By Negative Or Positive Feedback? Explain Your
 diabetestalk.netFeedback hormones negative loop endocrine physiology system control stress pathways hormone glucocorticoid regulation release anatomy gland adrenal hypothalamus glucocorticoids loops. Blood glucose control level summary concentration. Hormones · anatomy and physiology
diabetestalk.netFeedback hormones negative loop endocrine physiology system control stress pathways hormone glucocorticoid regulation release anatomy gland adrenal hypothalamus glucocorticoids loops. Blood glucose control level summary concentration. Hormones · anatomy and physiology